Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles from Leea coccinea leaves on Staphylococcus aureus
Main Article Content
Abstract
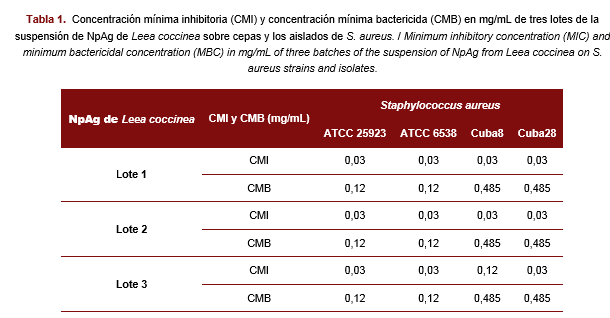
Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus represent a problem for animal and human health. This work was aimed to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of silver nanoparticles (NpAg) obtained by green synthesis with Leea coccinea leaf extract on Staphylococcus aureus strains and methicillin resistant isolates. Three batches of NpAg from Leea coccinea were evaluated on two S. aureus strains and two methicillin resistant isolates, by the serial dilution method, for MIC and MBC determination. NpAg from Leea coccinea showed antibacterial activity against resistant strains and isolates of S. aureus, with MIC values for the three batches mostly coinciding at 0.03 mg/mL for all the strains and isolates. MBC values in the three batches agreed and differences were observed between the values for resistant isolates (0.485 mg/mL) and strains (0.12 mg/mL). These results demonstrate the antibacterial activity of NpAg from Leea coccinea on this pathogen, demonstrating its potential as an alternative to antibiotic resistance and creating the basis for further studies for its application as an antibacterial agent.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
National Center for Animal and Plant Health (CENSA)References
Adhwa Masimen M, Harun N, Maulidiani M, Wan Ismail W. Overcoming Methicillin-Resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using antimicrobial peptides-silver nanoparticles. Antibiotics. 2022;11(951): 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070951.
Swolana D, Wojtyczka RD. Activity of silver nanoparticles against Staphylococcus spp. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022;23(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084298.
FAO, UNEP, WHO, WOAH. One Heath Joint Plan of Action (2022-2026). Working together for the health of humans, animals, plants and the environment. Rome. 2022. https://doi.org/10.4060/cc2289en.
Tacconelli E, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Harbarth S, Mendelson M, Monnet DL, et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2017;18(3): 318-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30753-3.
Novelles T, Travieso C, Ortega AR, Pita BA, López MC, Pérez LD, et al. Biosynthesis of fluorescent silver nanoparticles from Leea coccinea leaves and their antibacterial potentialities against Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. phaseoli. Bioresources and Bioprocessing. 2021;8(3). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-00354-2.
Baez M, Collaud A, Espinosa I, Perreten V. MRSA USA300, USA300-LV and ST5-IV in pigs, Cuba. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 2017;49(2): 259-261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.12.001.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically-M07. CLSI. 11th ed. 2018; 1-60. https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m07.
Mohammadlou M, Maghsoudi H, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H. A review on green silver nanoparticles based on plants: Synthesis, potential applications and eco-friendly approach. International Food Research Journal. 2016;23(2): 446-463. http://ifrj.upm.edu.my/23(02)2016/(2).pdf
Roy A, Bulut O, Some S, Mandal AK, Yilmaz MD. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Advances. 2019;9(5): 2673-2702. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08982e.
Nandhini P, Kumar P, Mickymaray S, Alothaim AS, Somasundaram J, Rajan M. Recent developments in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) treatment: A review. Antibiotics. 2022;11(5): 1-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050606.