Tasa de preñez de novillas Nelore bajo Inseminación Artificial combinada con suplementación mineral y vitamínica
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
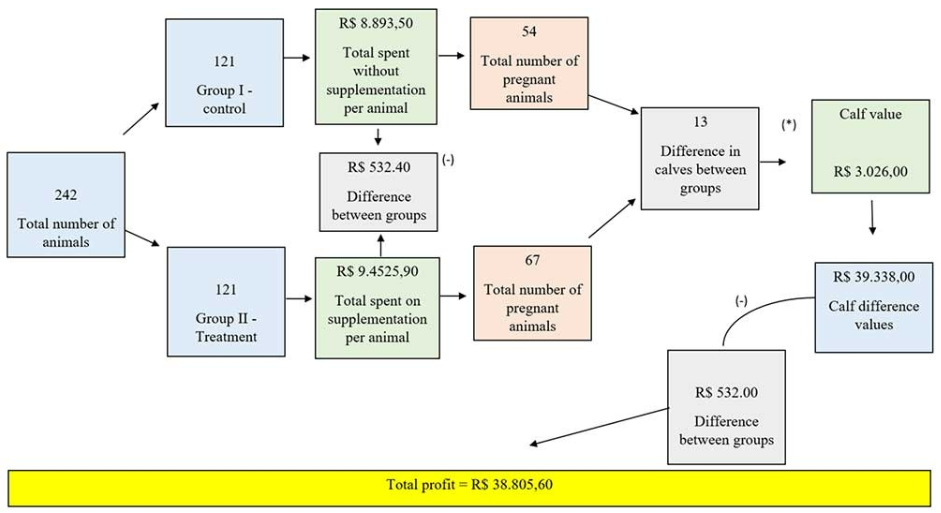
El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la tasa de preñez de novillas Nelore sometidas a inseminación artificial combinada con suplementación mineral y vitamínica. El estudio se realizó en una propiedad rural del municipio de Uruará, en el estado de Pará. Se utilizaron un total de 242 novillas Nelore, de 24 meses de edad, con un peso promedio de 320±2,5 kg. Las novillas se dividieron en un grupo control (n = 121 animales) y un grupo tratado (n = 121 animales) tratados con suplementación vitamínico mineral (Anabolic®) a una dosis de 10 mL por animal, por vía subcutánea, al inicio (D0) del protocolo de Inseminación Artificial a Tiempo Fijo (IATF). El diagnóstico de embarazo se realizó mediante ecografía. Se calculó la tasa de embarazo, así como el análisis económico del uso del suplemento. La tasa de preñez de los grupos se contrastó mediante análisis de comparación de proporciones esperadas mediante la prueba de chi-cuadrado con correcciones de continuidad al 5 % de significancia. Los resultados de las tasas de embarazo fueron del 44,62 % para el grupo control y del 55,38 % para el grupo tratado (p > 2373). Sin embargo, en términos económicos, las vacas suplementadas generaron 13 terneros más que el grupo control, con una ganancia bruta de 38.805,60. La suplementación con vitaminas minerales administrada antes de la IATF no promovió un aumento significativo en la tasa de preñez en vacas Nelore con una condición corporal moderada. Sin embargo, en el sesgo económico, la adopción del protocolo de suplementación proporcionó ganancias considerables al productor.
Detalles del artículo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cual estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) que prohíbe el uso comercial de sus publicaciones y permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y la primera publicación en esta revista. Bajo esta licencia el autor será libre de:
- Compartir — copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato
- Adaptar — remezclar, transformar y crear a partir del material
- El licenciador no puede revocar estas libertades mientras cumpla con los términos de la licencia
Bajo las siguientes condiciones:
- Reconocimiento — Debe reconocer adecuadamente la autoría, proporcionar un enlace a la licencia e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo de cualquier manera razonable, pero no de una manera que sugiera que tiene el apoyo del licenciador o lo recibe por el uso que hace.
- NoComercial — No puede utilizar el material para una finalidad comercial.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales o medidas tecnológicas que legalmente restrinjan realizar aquello que la licencia permite.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).
Citas
Gonçalves LDPN, Prado AJ, Pacheco A, Almeida YEFD, Baruselli PS, Silva WCD, Neves KAL. Reproductive Efficiency of Nelore Cows in Fixed-Time Artificial Insemination Programs with Early Resynchronization. Veterinary Sciences, 2025;12(1):27.
Silva FPD, Neves KAL, Correa FR, Silva LK, Batista HR, Silva WC, Caruso NM, Minervino AHH. Follicular Dynamics and Pregnancy Rate in Nelore Heifers Submitted to Fixed-Time Artificial Insemination Protocols (FTAI). Veterinary Sciences. 2022;9(8):377.
Silva WCD, Silva JARD, Camargo-Júnior RNC, Silva ÉBRD, Santos MRPD, Viana RB, Silva AGM, Silva CMG, Lourenço-Júnior JDB. Animal welfare and effects of per-female stress on male and cattle reproduction-A review. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 2023;10(1):1083469.
Silva WCD, Printes OVN, Lima DO, Silva ÉBRD, Santos MRPD, Camargo-Júnior RNC, Barbosa AVC, Silva JAR, Silva AGM, Silva LKX, Araújo CV, Britto EM, Lourenço-Júnior JDB. Evaluation of the Temperature and Humidity Index (THI) to support the implementation of a rearing system for ruminants in the Western Amazon. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 2023;10(1):1198678.
Hallerman EM, Bredlau JP, Camargo LSA, Dagli MLZ, Karembu M, Ngure G, Wray-Cahen D. Towards progressive regulatory approaches for agricultural applications of animal biotechnology. Transgenic Research, 2022;31(2):167-199.
Nagy PP, Skidmore JA, Juhasz J. Intensification of camel farming and milk production with special emphasis on animal health, welfare, and the biotechnology of reproduction. Animal Frontiers, 2022;12(4):35-45.
Bourdon G, Cadoret V, Charpigny G, Couturier-Tarrade A, Dalbies-Tran R, Flores MJ, Jouneau A. Progress and challenges in developing organoids in farm animal species for the study of reproduction and their applications to reproductive biotechnologies. Veterinary research, 2021;52:1-20.
Oliveira BS, Silva KZ, Batista HR, Silva WC, Júnior RNCC. Estudo retrospectivo das taxas de prenhez obtidas com uso de protocolos de inseminação artificial em tempo fixo (IATF) em vacas suplementadas com hormônio liberador de gonadotrofina (GNRH)-Mini Revisão. Brazilian Journal of Development. 2021;7(12):119023-119031.
Lazarini IS, Paula-Santos U, Vinhote BP, Silva WC, Júnior RNCC. Prenhez em novilhas Nelore induzidas à puberdade, criadas na Amazônia Oriental Pregnancy in puberty-induced Nelore heifers, breeding in the eastern Amazon. Brazilian Journal of Development. 2021;7(12):119012-119022.
Oliveira VS, Silva WC, Pina-Maia T, Silva, LKX. Is there a correlation between the body condition score and the pregnancy rate of Nelore cows submitted to FTAI in the Eastern Amazon? CES Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia. 2022;17(2):8-18.
D’occhio MJ, Baruselli PS, Campanile G. Influence of nutrition, body condition, and metabolic status on reproduction in female beef cattle: A review. Theriogenology. 2019;125(1):277-284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.11.010
Abera M, Yusuf Mummed Y, Eshetu M, Pilla F, Wondifraw Z. Physiological, biochemical, and growth parameters of Fogera cattle calves to heat stress during different seasons in sub-humid part of Ethiopia. Animals, 2021;11(4):1062.
Izquierdo AC, Reyes AEI, Lang GR, Oaxaca JS, Liera JEG, Mancera EAV, Sánchez RS. Nutrition and Food in the Reproduction of Cattle. European Journal of Agriculture and Food Sciences, 2021;3(3):21-33.
Priya P, Kumari P, Ballabh J, Ikram M, Jain G, Prasad R, Joshi R. Nutritional Deficiency of Farm Animals: A Review. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences, 2022;349-354.
Arthington JD, Ranches J. Trace mineral nutrition of grazing beef cattle. Animals, 2021;11(10):2767.
Younis M, El-Ashker M, El-Diasty M, Youssef MA, El-Khodery S. Oxidative Stress in Transition Dairy Cattle: Current Knowledge and the Potential Impact of Supplementing Organic Trace Elements. Asian Journal of Research in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2021;7(1):1-21.
Kotsampasi B, Karatzia MA, Tsiokos D, Chadio, S. Nutritional Strategies to Alleviate Stress and Improve Welfare in Dairy Ruminants. Animals, 2024:14(17):2573.
Martorano LG, Vitorino MI, Silva BPPC, Lisboa LS, Sotta ED, Reichardt K. Climate conditions in the eastern amazon: Rainfall variability in Belem and indicative of soil water deficit. African Journal of Agricultural Research. 2017;12(21):1801-1810.
Ayres H, Ferreira RM, Torres-Júnior JRS, Demétrio CGB, Lima CG, Baruselli PS. Validation of body condition score as a predictor of subcutaneous fat in Nelore (Bos indicus) cows. Livestock Science. 2009;123(3):175-179.
Anabolic®. https://www.noxon.com.br/anabolic/. Accessed on: January 20, 2025.
Ren SQ, Wang JW, Chen HY, Xu MQ, Jiang H, Gao Y, et al. Effect of vitamin E on apoptosis and proliferation of bovine granulosa cells using cx43. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine. 2016;43(16).
Pinheiro VG, Souza AF, Pegorer MF, Satrapa RA, Ereno RL, Trinca LA, Barros CM. Effects of temporary calf removal and eCG on pregnancy rates for timed insemination in postpartum Nelore cows treated with progesterone. Theriogenology. 2019;71(19):519-524.
Binelli M, Machado R, Bergamaschi MACM, Bertran CM. Manipulation of ovarian and uterine function to increase conception rates in cattle. Journal Animal Reproduction. 2019;6(1):125-134.
Silva FPD, Neves KAL, Correa FR, Silva LK, Batista HR, Silva WC, Caruso NM, Minervino AHH. Follicular Dynamics and Pregnancy Rate in Nelore Heifers Submitted to Fixed-Time Artificial Insemination Protocols (FTAI). Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(8):377.
Gouvêa VN, Colli MHA, Junior WAG, Motta JCL, Acedo TS, Tamassia LFM, Elliff FM, Mingoti RD, Baruselli PS. The combination of β-carotene and vitamins improve the pregnancy rate at first fixed-time artificial insemination in grazing beef cows. Livestock Science. 2018;217(1):30-36.
Sales JNS, Pereira RVV, Bicalho RC, Baruselli OS. Effect of injectable copper, selenium, zinc and manganese on the pregnancy rate of crossbred heifers (Bos indicus × Bos taurus) synchronized for timed embryo transfer. Livestock Science. 2011;142(1-3):59-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2011.06.014.
Mundell LR, Jaeger JR, Waggoner JW, Stevenson JS, Grieger DM, Pacheco LA, Bolte JW, Aubel NA, Eckerle GJ, Macek MJ, Ensley SM, Havenga LJ, Olson KC. Effects of prepartum and postpartum bolus injections of trace minerals on performance of beef cows and calves grazing native range. The Professional Animal Science. 2012;28(1):82-88. https://doi.org/10.15232/S1080-7446(15)30318-1.
Stokes RS, Ralph AR, Mickna AJ, Chapple WP, Schroeder AR, Ireland FA, Shike DW. Effect of an injectable trace mineral at the initiation of a 14 day CIDR protocol on heifer performance and reproduction. Translational Animal Science. 2017;1(4):458-466. https://doi.org/10.2527/tas2017.0050.
Arthington JD, Martins PGMA, Moriel P, Havenga LJ. Effects of injectable trace minerals at the start of the breeding season on attainment of pregnancy in commercial beef cows. Journal Animal Science. 2014;92(Suppl. 2):723-724.
Willmore CJ, Hall JB, Harrison S, Drewnoski ME. Effect of a trace mineral injection on pregnancy rate of Angus beef heifers when synchronized using the 14- day controlled internal drug-releasing insert-prostaglandin F2α protocol at a commercial feedlot. The Professional Animal Science. 2015;31(6):588-592. https://doi.org/10.15232/pas.2015-01412
Gonzalez-Maldonado J, Rangel-Santos R, Rodriguez-de Lara R, Garcia-Pena O. Effect of an injectable trace mineral complex supplementation on development of ovarian structures and serum copper and zinc concentration in over-conditioned Holstein cows. Animal Reproduction Science. 2017;181(1):57-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2017.03.015
Stokes RS, Volk MJ, Ireland FA, Gunn PJ, Shike DW. Effect of repeated trace mineral injections on beef heifer development and reproductive performance. Journal Animal Science. 2018;96(9):3943-3954. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/sky253.