Antifungal activity of saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. against agriculturally important plant pathogenic fungi
Main Article Content
Abstract
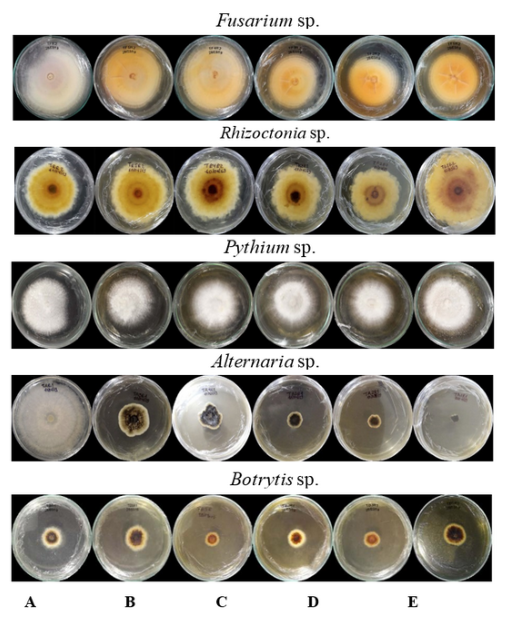
The aim of the present work was to determine the antifungal activity of saponins extracted from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. against five phytopathogenic fungi of agricultural importance. The saponin extracts were obtained by the Soxhlet method described by Amores in 2022 and the concentrations were determined by the UV-VIS spectrophotometric method. The biological activity of the aqueous extracts of saponins was tested on the fungi Fusarium sp., Rhizoctonia sp., Pythium sp., Alternaria sp., and Botrytis sp. at concentrations of 100, 87.5, 75, 50, and 37.5 % using the Potato-Dextrose-Agar culture medium poisoning method (Difco, pH 5.5) under a completely randomized design. The highest inhibitory effect was evident on the growth of Alternaria sp. with 89.5 % at 100 % concentration of saponins. The fungi Fusarium sp., Rhizoctonia sp., Pythium sp., and Botrytis sp. were not well controlled by the metabolic effect of the concentrations tested. These findings provide a new alternative for the biocontrol of this fungus, causal agent of economic losses in different crops in Ecuadorian agriculture.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cual estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) que permite a terceros compartir la obra, siempre que se indique su autor y la primera publicación en esta revista. Bajo esta licencia el autor será libre de:
- Compartir — copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato
- Adaptar — remezclar, transformar y crear a partir del material
- El licenciador no puede revocar estas libertades mientras cumpla con los términos de la licencia
Bajo las siguientes condiciones:
- Reconocimiento — Debe reconocer adecuadamente la autoría, proporcionar un enlace a la licencia e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo de cualquier manera razonable, pero no de una manera que sugiera que tiene el apoyo del licenciador o lo recibe por el uso que hace.
- NoComercial — No puede utilizar el material para una finalidad comercial.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales o medidas tecnológicas que legalmente restrinjan realizar aquello que la licencia permite.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).
References
Basantes F, Aragón JP, Albuja M. Cultivos andinos de importancia agroproductiva y commercial en la zona 1 del Ecuador. Editorial Universidad Técnica del Norte, Ibarra-Ecuador. 2022; 192pp.
Hernández-Ledesma B. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) as a source of nutrients and bioactive compounds: a review. Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease. 2019; 2 (3): 2747.
Chaudhary N, Walia S, Kumar R. Functional composition, physiological effect and agronomy of future food quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): A review. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 2023; 118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2023.105192
Plata G, Gandarillas A. Enfermedades más importantes que afectan al cultivo de la quinua en Bolivia. Revista de Agricultura. 2014; 54:19-28.
Casas MM, Cristancho JA. Determinación de la actividad plaguicida de las saponinas presentes en la cáscara de las semillas de la especie vegetal quinua (Chenopodium quinoa) para aplicación en cultivos de fresa (Fragaria albión). Tesis de Tecnología en Química Industrial. Bogotá, Colombia. 2022; 56 pp.
El Hazzam K, Hafsa J, Sobeh M, Mhada M, Taourirte M, Kacimi KEL, et al. An insight into saponins from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd): A review. Molecules. 2020; 25 (5): 1-22.
Singh B, Kaur A: Control of insect pests in crop plants and stored food grains using plant saponins: a review. Food Science and Technology. 2018; 87: 93-101.
Villacrés E, Quelal M, Galarza S, Iza D, Silva E. Nutritional value and bioactive compounds of leaves and grains from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). Plants. 2022; 11 (2): 1-11.
Stuardo M, San Martin R. Antifungal properties of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) alkali treated saponins against Botrytis cinerea. Industrial Crops and Products. 2008; 27: 296-302.
Apaza R, Smeltekop H, Flores Y, Almanza G, Salcedo L. Efecto de saponinas de Chenopodium quinoa Willd contra el fitopatógeno Cercospora beticola Sacc. Rev. Protección Veg 2016; 31(1): 63-69.
Dean J. Extraction Techniques in Analytical Sciences. [S.L.]: John Wiley & Sons, 2010; 167 pp.
Monje CY, Raffaillac JP. Determinación de saponina total en quinua (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) método Espectrofotométrico. Memoria IV Congreso Nacional de la Asociación Boliviana de Protección Vegetal. Oruro, 5 al 7 de abril de 2006. C.E.A.C. -Dpto.Fitotecnia-FCAPV UTO. ABPV. Oruro, Bolivia, 2006; pp. 217-218
Gianna V. Extracción, cuantificación y purificación de saponinas de semillas de Chenopodium quinoa Willd provenientes del noroeste argentino. [Tesis Doctoral]. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales, 2013; 116 pp. Argentina.
StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 12. 2014, www.statsoft.com.
McCartney NB, Ahumada MI, Muñoz MP, Rosales IM, Fierro AM y Chorbadjian RA. Effects of saponin-rich quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) bran and bran extract in diets of adapted and non-adapted quinoa pests in laboratory bioassays. Ciencia e Investigación Agraria 2019; 46 (2): 125-136.
San Martin R, Ndjoko K, Hostettmann K. Novel molluscicide against Pomacea caniculata based on quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) saponins. Crop Protection. 2008; 27: 310-317.