Ecological impact of Raoiella indica Hirst on the mite fauna of San José de las Lajas municipality, Mayabeque, Cuba
Main Article Content
Abstract
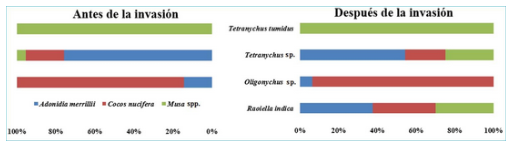
The structure of the mite communities were compared in San José de las Lajas municipality, Mayabeque province, Cuba, before and after the introduction of Raoiella indica Hirst to establish its ecological impact on the mite fauna present on selected species of the families Arecaceae and Musaceae . The selected botanical species were Cocos nucifera L., Adonidia merrillii (Becc.) Becc., Dypsis lutescens (H. Wendl.) Beentje & J. Dransf., Roystonea regia O.F. Cook, and Musa spp. The abundance of the mites detected by functional group was calculated and different ecological indices were applied. The introduction of R. indica into San José de las Lajas municipality caused a reduction of the associated-mite richness in the evaluated plant species, which was particularly marked in coconut and garden palm due to the reduction of predatory mites. A significant increase in the family Tenuipalpidae was observed, due to the high populations of R. indica recorded on C. nucifera, A. merrillii and Musa spp., to the detriment of representatives of the families Tetranychidae and Eriophyidae, which were majorities in the first sampling period. The existence of a rearrangement of the mite species and their abundance was demonstrated, being evidenced by the reduction of species diversity and the increase of dominance, in response to population increases of the invasive exotic mite, which could cause imbalances and affect biodiversity over time.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cual estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) que permite a terceros compartir la obra, siempre que se indique su autor y la primera publicación en esta revista. Bajo esta licencia el autor será libre de:
- Compartir — copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato
- Adaptar — remezclar, transformar y crear a partir del material
- El licenciador no puede revocar estas libertades mientras cumpla con los términos de la licencia
Bajo las siguientes condiciones:
- Reconocimiento — Debe reconocer adecuadamente la autoría, proporcionar un enlace a la licencia e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo de cualquier manera razonable, pero no de una manera que sugiera que tiene el apoyo del licenciador o lo recibe por el uso que hace.
- NoComercial — No puede utilizar el material para una finalidad comercial.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales o medidas tecnológicas que legalmente restrinjan realizar aquello que la licencia permite.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).
References
Verle-Rodrigues JC, Ochoa R, Carrillo D. Impacts of continental invasion of Raoiella indica in the America. Zoosymposia, 080-080. In Zhang Z-Q, Fan Q-H, Heath ACG, Minor MA (Eds). 2022. Acarological Frontiers: Proceedings of the XVI International Congress of Acarology (1-5 Dec. 2022, Auckland, New Zealand). Magnolia Press, Auckland 328 pp.
Castro EB, Mesa NC, Feres RJF, Moraes GJ de, Ochoa R, Beard JJ, Demite PR. Tenuipalpidae Database. 2021. Disponible en: http://www.tenuipalpidae.ibilce.unesp.br. (Consultado: 28 de abril de 2022)
Talor B. Raoiella indica (red palm mite). CABI Compendium, Datasheet. 2022. [May 15 2022]. https://doi.org/10.1079/cabicompendium.46792. (Consultado: 28 de abril de 2022)
Ramos M, Rodríguez H. Fitoácaros exóticos y endémicos de importancia agrícola en Cuba. Centro Nacional de Áreas Protegidas. 2017, ISBN: 978-959-287-081-9. 260 pp.
Flores-Galano G, Montoya-Ramos A, Gonzálbez-Colina H, Rodríguez-Morell H. Biología y tabla de vida de Raoiella indica Hirst. (Acari: Tenuipalpidae) sobre cocotero (Cocos nucifera L.). Rev Protección Veg. 2018; 33 (2): 1-8.
Rodríguez H, Alonso D, García A, Chico R, Hastie E, Ramos M. Ácaros depredadores asociados a Raoiella indica Hirst (Acari: Tenuipalpidae) en San José de las Lajas, Mayabeque. Métodos en Ecología y Sistemática (Costa Rica). 2016; 11(1):12-23.
Posos-Ponce P, Flores-Galano G, Rodríguez-Morell H, Montoya-Ramos A, Monroy-Reyes B. Capacidad depredadora de Amblyseius largoensis Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae) sobre Raoiella indica Hirst (Acari: Tenuipalpidae) en condiciones de laboratorio. Revista Entomología Mexicana. 2019; 6: 8-13.
Alonso D, Hernández R, Chico R, Miranda I, Rodríguez H. Incidencia de Raoiella indica Hirst y Tetranychus tumidus Banks en diferentes genotipos de plátano (Musa spp.). Métodos en Ecología y Sistemática. (Costa Rica). 2015; 10(2):72-82.
Rodríguez-Morell H, Alonso-Rodríguez D, Ysidro-Hernández M, Pérez-Madruga Y. Densidad e índice estomático en genotipos de Musa con respuesta diferencial ante Raoiella indica Hirst. Rev Protección Veg. 2021; 36(3): 1-4.
R Core Team. Biodiversity R. Biodiversity Package for R Version 3.6. GUI for biodiversity and community ecology analysis. 2011. URL http://www.r-project.org/diversity. (Consultado: 28 de abril de 2022)
Di Rienzo JA, Casanoves F, Balzarini MG, Gonzalez L, Tablada M, Robledo CW. InfoStat versión 2020. Grupo InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. Disponible en: http://www.infostat.com.ar. (Consultado: 28 de abril de 2022)
Kane E, Ochoa R, Mathurin G, Erbe E. Raoiella indica Hirst (Acari: Tenuipalpidae): an island hopping mite pest in the Caribbean. 2005. (En línea). Disponible en: http://www.sel.barc.usda.gov/acari/PDF/TrinidadHandout.pdf. (Consultado: 13 de marzo de 2021)
Calvet EC, Lima DB, Melo JWS, Gondim MCG Jr. The expansion of invasive mite Raoiella indica can be improved by coexistence with Oligonychus pratensis. Annals Applied Biol. 2022; https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12773
Barros MEN, Lima DB, Mendes JA, Gondim MCG Jr., Melo JWS. The establishment of an invasive pest mite, Raoiella indica, affects mite abundance and diversity on coconut plants. Sys Appl Acarol. 2020; 25(5):881-894. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.25.5.9
Ferragut F, Garzón-Luque E, Pekas A. The invasive spider mite Tetranychus evansi (Acari: Tetranychidae) alters community composition and host-plant use of native relatives. Exp Appl Acarol. 2013; 60 321-341.