Potentialities of Lonchocarpus nicou root powder for management of Neoconocephalus sp.
Main Article Content
Abstract
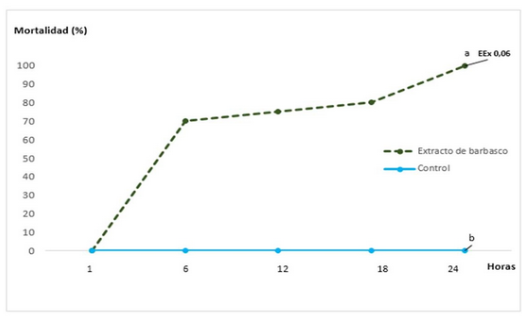
The objective of this research was to evaluate the potential of Lonchocarpus nicou Aublet root powder for management of Neoconocephalus sp (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae). Fresh roots of L. nicou collected from Ecuatorian Amazonia were processed. Under laboratory conditions, the lethal toxicity of the root powder on adults was evaluated. A random design with five repetitions was used to evaluate the dosage of 6, 25 g. l-1; a negative control was included and the results were processed by a comparison of proportions. The L. nicou root powder showed a lethal toxic effect on adults of Neoconocephalus sp. Inanition, uncoordinated movement, paralysis and 70 % of insect mortality was observed after 6 hours. Population death of 100 % after 24 hours with statistically significant differences compared with the control was found. Based on the high toxicity on adults, the root extract of L. nicou shows potential to be developed as pesticides intended for management of Neoconocephalus sp.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cual estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) que permite a terceros compartir la obra, siempre que se indique su autor y la primera publicación en esta revista. Bajo esta licencia el autor será libre de:
- Compartir — copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato
- Adaptar — remezclar, transformar y crear a partir del material
- El licenciador no puede revocar estas libertades mientras cumpla con los términos de la licencia
Bajo las siguientes condiciones:
- Reconocimiento — Debe reconocer adecuadamente la autoría, proporcionar un enlace a la licencia e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo de cualquier manera razonable, pero no de una manera que sugiera que tiene el apoyo del licenciador o lo recibe por el uso que hace.
- NoComercial — No puede utilizar el material para una finalidad comercial.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales o medidas tecnológicas que legalmente restrinjan realizar aquello que la licencia permite.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).
References
Eades DC, Otte D, Cigliano MM, Braun H. Orthoptera Species File. Version 5.0/5.0. 2020. Available from: https://orthoptera.speciesfile.org/.
SINA. Subfamily Copiphorinae: Coneheaded katydids. Singing Insects of North America. University of Florida. 2022. Available from: http://orthsoc.org/sina/index.htm.
Sattar A, Karim Ulah, Abdul Ahad, Yousaf M. Insect pests of sunflower in N.W.F.P, Pakistan. Pak J Agric Res. 1984;5(4):239-241.
CABI. Neoconocephalus affinis (rattler conehead katydid). CABI Compendium. 2023. Available from: http://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/49032471.
Torres GA, Sarria GA, Varón F, Martínez G. Evidencias circunstanciales de la asociación de especies de la familia Tettigoniidae con el desarrollo de lesiones iniciales de la pudrición del cogollo de la palma de aceite. Palmas. 2008;49(3):53-61.
Cadena OJ, Gutiérrez Y, Bacca T. Common Orthoptera from Pastaza, Ecuador. Available from: https://fieldguides.fieldmuseum.org/.
UC IPM. Pest management guidelines: Citrus. California.UC ANR Publication 3441. 2022. University of California, USA. Available from: http://ipm.ucanr.edu/?src=www2.
Wahid H, Stefan D, Jaronski T, Schell S. Control of Pest Grasshoppers in North America. Insects. 2020 Aug 24;11(9):566. DOI: 10.3390/insects11090566.
Martín NJ, Pérez G. Agricultural productive evaluation of four sectors from Pastaza province in the Ecuadorian Amazonia. Cultivos Tropicales. 2012 Jul;30(1):5-10. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/index.php/ediciones/article/view/126.
Torres Morocho DM, Orea Igarza U, Brito Vallina ML, Cordero Machado E. Estudio de la extracción del follaje de Barbasco (Lonchocarpus nicou) como fuente biocida (en condiciones de la Amazonía en Ecuador). Rev Cienc Téc Agr. diciembre de 2013;22(4):41-9. Available from: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S2071-00542013000400007&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=es.
Vélez A, Fajardo E, Morán Bajaña JT, Centanaro Quiroz PH, Cartagena Faytong MI, Cruz Romero CE, et al. Efecto biocida del fruto del barbasco (Lonchocarpus nicou) en el control del caracol (Pomacea canaliculata) en el arroz en Naranjal - Ecuador. ProSciences. 2019;3(20):1-4. DOI: 10.29018/issn.2588-1000vol3iss20.2019pp1-4
Vílchez EJ, Sánchez GV. Uso de la Rotenona (Lonchocarpus nicou) para controlar plagas de la col en Lima. Rev. Per. Ent. 1993;36:65-68. Available from: https://www.revperuentomol.com.pe/index.php/rev-peru-entomol/article/view/1051
Mariños C, Castro J, Nongrados D. Efecto biocida del «barbasco» Lonchocarpus utilis (Smith, 1930) como regulador de larvas de mosquitos. Rev.per.biol. 2004;11(1):87-94. DOI: 10.1079/pwkb.species.49032471
Huang CW, Lin KM, Hung TY, Chuang YC, Wu SN. Multiple Actions of Rotenone, an Inhibitor of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain, on Ionic Currents and Miniature End-Plate Potential in Mouse Hippocampal (mHippoE-14) Neurons. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2018;47:330-343. DOI: 10.1159/000489810
Fang NB, Casida JE. Anticancer action of cube insecticide: Correlation for rotenoid constituents between inhibition of NADH: Ubiquinone oxidoreductase and induced ornithine decarboxylase activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:3380-3384. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3380
Iannone JA, Murrugara Y. Efecto del nin y rotenona en las poblaciones de Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) y en dos especies de áfidos (Homoptera: Aphididae) en el cultivo de tomate en Inca, Perú. Folia Entomol. Mex. 2002;41(2):119-128.
Iannone J. Efecto insecticida de cuatro extractos botánicos sobre la polilla de la papa Phthorimaea operculella (Zeller) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) en el Perú. Entomotropica. 2003;18(2):95-105.
Ren L, Zheng G, Chen B, He L, Liao Y, Chen B. Evaluation of ten botanical insecticides against the sweet potato Weevil, Cylas formicarius (Fabricius, 1798) (Coleoptera: Brentidae). Afr J Agric Res. 2020;16(11):1531-1539. DOI: 10.5897/AJAR2020.15054
Han L, Gao L, Hao Z, Zhao K, Zhang W, Chen J, et al. Effect of rotenone induced stress on physiologically active substances in adult Aphis gycines. PLoS One. 2020;15(6). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234137
Booth AJ, Moss S, Weyl OLF. Effect on gill respiring and plastron respiring insects. Afr J Aquat Sci. 2015;40(1):95-100. DOI: 10.2989/16085914.2014.986432
Wang Y, Huang X, Chang BH, Zhang Z. Growth Performance and Enzymatic Response of the Grasshopper, Calliptamus abbreviatus (Orthoptera: Acrididae), to Six Plant-Derived Compounds. J Insect Sci. 2020;20(3):14. DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/ieaa049
Jiménez E, Tovar J, Mosquera OM, Cardozo F. Actividad neuroprotectora de Solanum ovalifolium (Solanaceae) contra la toxicidad inducida por rotenona en Drosophila melanogaster. Rev Fac Cienc Básicas. 2017;13(1):26-34. DOI: 10.18359/rfcb.2751
Zhang W, Ren H, Sun F, Shen T, Yuan S, Gao X, et al. Evaluation of the Toxicity of Chemical and Biogenic Insecticides to Three Outbreaking Insects in Desert Steppes of Northern China. Toxins. 2022;14(8):546. DOI: 10.3390/toxins14080546